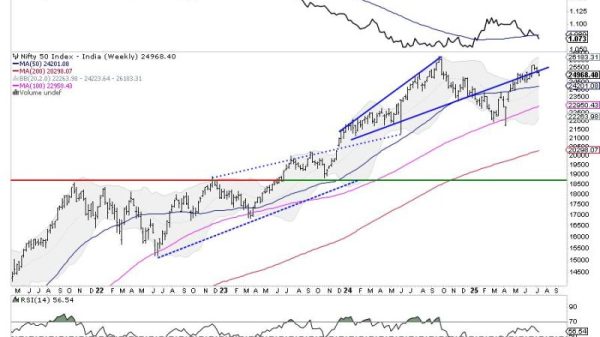
An electric motorcycle, made by Swedish-Kenyan manufacturer Roam completed a 6,000-kilometer (3,700-mile) journey from Nairobi, Kenya, to Stellenbosch, South Africa, in 17 days, using only solar power.
While the world record for the longest electric motorcycle journey is 25,000 kilometers (11,300 miles), undertaken over 42 days in the US, Roam hopes that its stunt helps to prove the viability of renewable energy for long-distance travel even in remote areas with poor charging infrastructure.
The batteries were charged en route through a solar panel charging system carried in a support vehicle, which would drive ahead each day, stopping to charge up the batteries, so that when the bike caught up it could swap the dead battery for a fresh one. During the journey, the motorcycle model, the Roam Air, achieved its new single battery record range of 113 kilometers (70 miles), and on the trip’s last day, it traveled 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) in less than 18 hours.
Kituyi split the riding with Stephan Lacock, a postgraduate student at Stellenbosch University who is working on a powertrain simulation project to boost the Roam Air’s efficiency. Accompanied by two support vehicles, they set off on 29 September, traveling through Tanzania, Malawi, Zambia and Botswana, before arriving in Stellenbosch on the morning of 16 October. The team drove along highways and dirt tracks, stopping off at Victoria Falls and Chobe River, where they camped under the stars and among hippos.
On average the team covered around 400 kilometers (250 miles) per day, with about 80 kilometers (50 miles) per battery.
Cloud cover
The biggest challenge the team faced during the journey was the weather. “You can’t force the sun to shine,” says Kituyi, and at some points they ended up adapting their route so that they could escape cloud cover and have an opportunity to recharge the batteries.
While Roam wanted to demonstrate the potential of solar energy as a solution for powering bikes in areas that lack charging infrastructure, Kituyi says that most of Roam’s customers charge their bikes at home with energy from the grid. However, he insists that this mammoth journey would still be possible for people without a solar support car.
“Anywhere you can charge your phone, you can charge the bike,” he says. “That means with enough planning and lodging in hotels that have electricity, you are able to do this journey yourself.”
However, he adds that he’s not expecting many of Roam’s customers to travel cross-continent – rather, riders might need the bike to travel between rural areas and cities. The feat was about “showing the flexibility works,” he says, and countering range anxiety.
Accelerating market
The journey was a collaborative effort between Roam and Stellenbosch University, which launched an Electric Mobility Lab this month, dedicated to advancing sustainable transport solutions.
Roam donated two motorcycles to the lab to support research and develop the bikes further. Kituyi hopes that through powertrain efficiency tests and “accelerated testing,” which involves charging and discharging the battery multiple times a day, the startup will gain a better understanding of the life cycles of the bike and the battery.
He adds that “accelerated testing” requires special facilities, and in the past Roam has carried out these tests outside Africa, including in China. The lab will give Roam the opportunity to keep the testing within the continent, which he says will make it more reliable as it’s undertaken in a similar climate, as well as helping to build Africa’s electric vehicle (EV) market.
According to market research firm Mordor Intelligence, the African EV market is worth an estimated $16 billion, and it is projected to reach $25 billion by 2029. It claims this is driven by increased investment, rising EV sales, and government policies that encourage electrification. For example, Rwanda has eliminated import taxes on electric vehicles and is offering incentives for charging infrastructure development.
They added that African startups are dominating the space, since they have designed bikes to withstand local road conditions, do not rely on traditional charging infrastructure, and offer flexible payment options. Rwanda’s Ampersand currently has a fleet of almost 4,000 and expects this to surpass 40,000 by the end of 2026, whereas Spiro has over 18,000 e-bikes on the road across Kenya, Benin, Togo, Rwanda and Uganda, and has launched in Nigeria.
Roam, founded in 2017 and formerly known as Opibus, has seen this transition firsthand. It started by electrifying safari vehicles, before turning to buses and motorcycles. Today, motorcycles are its main focus and it produces around 40 bikes a day, according to Kituyi. Currently, the bikes are available to buy in greater Nairobi, and in early 2025, it will be expanding across the whole of Kenya, as well as entering Uganda and Rwanda.
“There is a big demand and constant growth of the market for motorcycles,” says Kituyi, adding that he has seen a gradual shift in people’s mindset. “They are getting more confident with the idea of stopping at a restaurant and asking them for electricity to charge their bike.”
He hopes that the recent expedition will help to build trust in EVs even further.